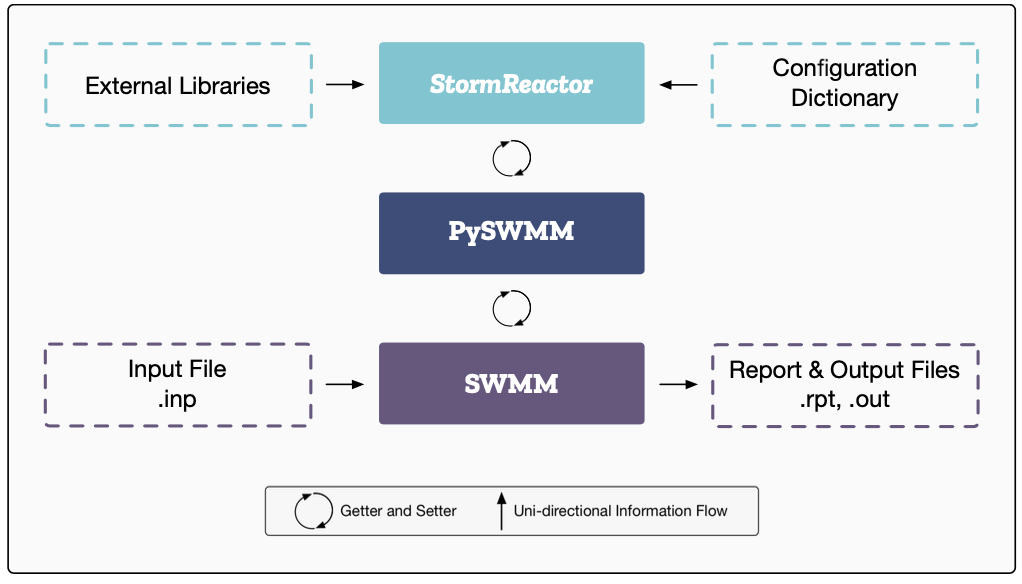
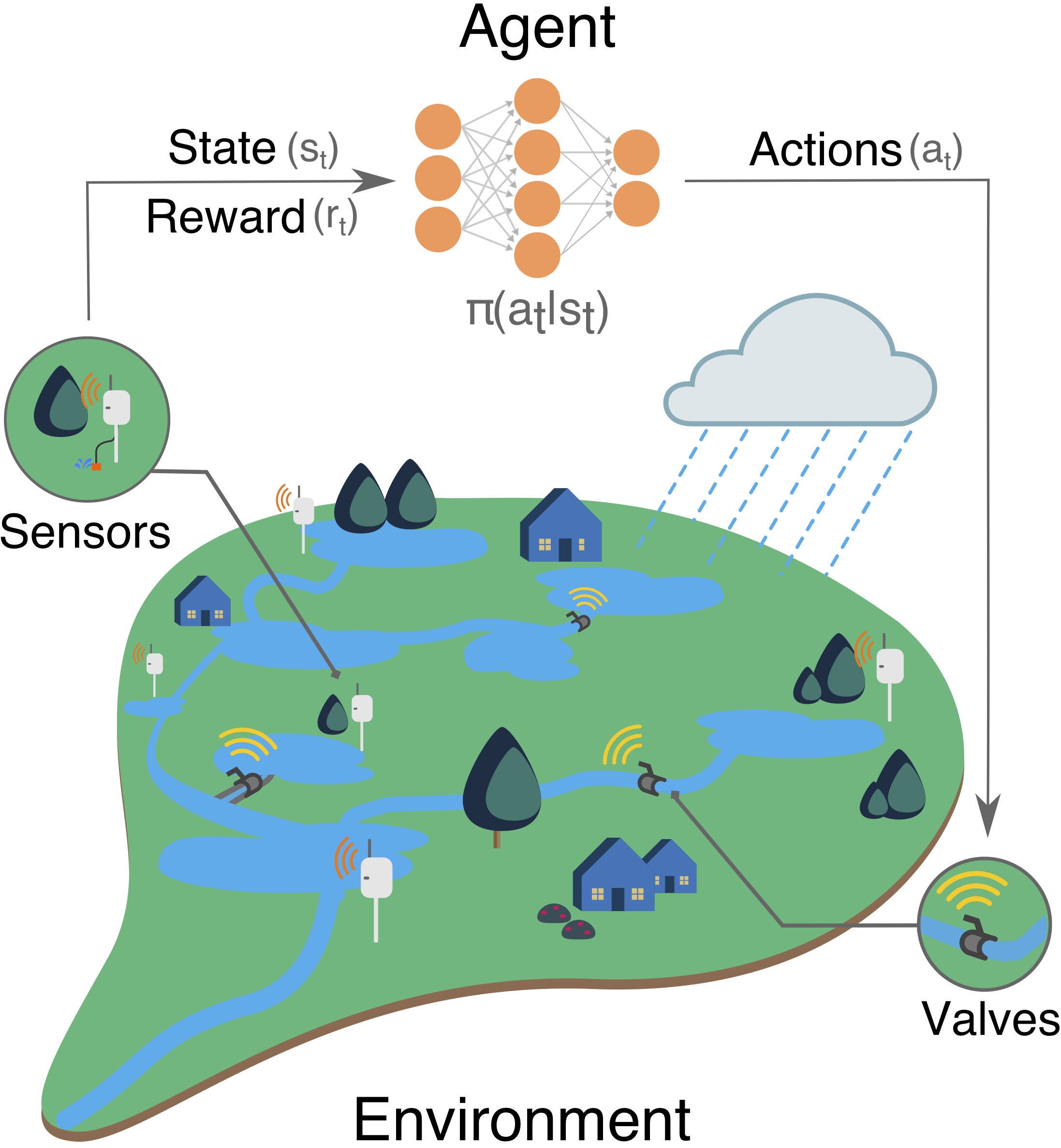
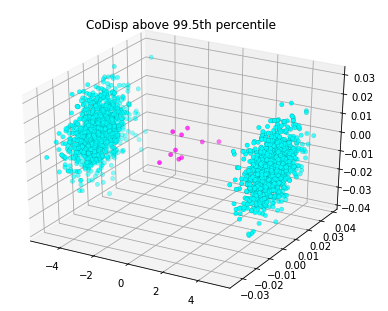
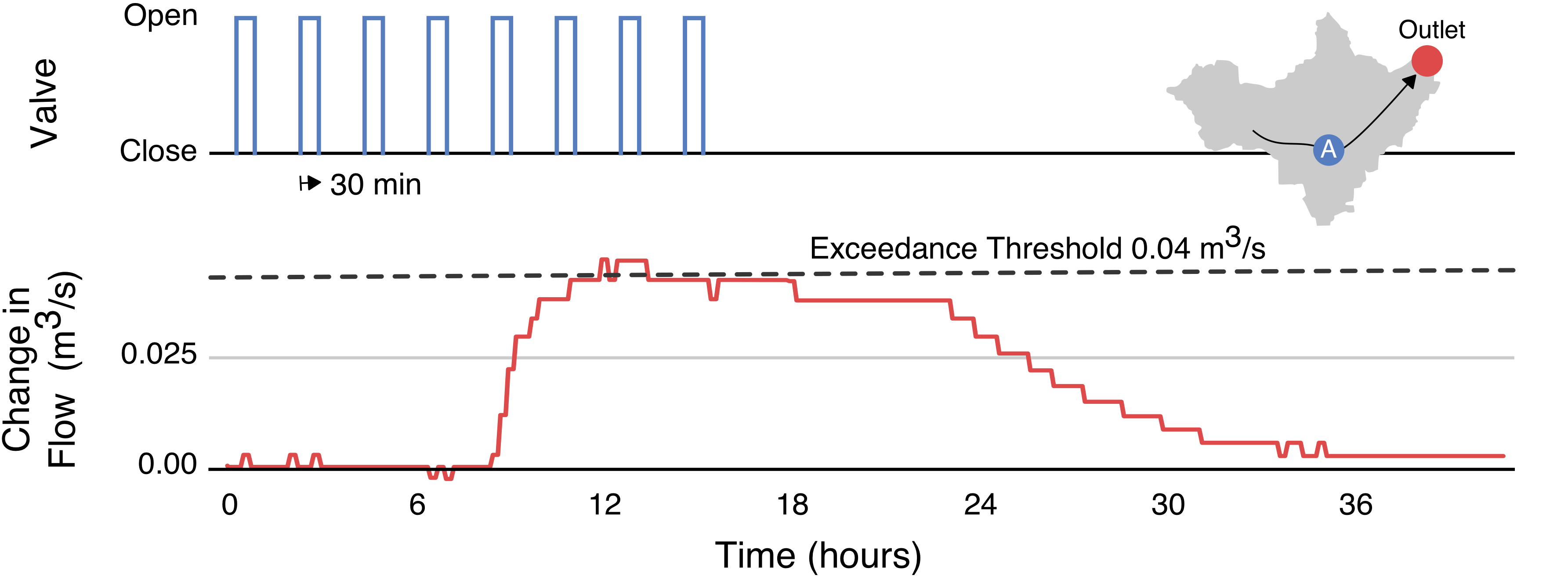
Hello! I am Abhiram Mullapudi (అభిరామ్ ముళ్లపూడి). I build digital water systems that integrate machine learning, wireless sensor networks, and physical modeling to improve the resilience of urban water infrastructure. I am currently working at Inframark as a Lead Data Scientist, where I develop scalable machine learning solutions for small and medium-sized water utilities. My interests lie in signal processing, probabilistic methods, and optimization for cyber-physical infrastructure systems. I write about some of these at randomstorms.substack.com. I am based in Washington, DC 🌸. During my free time, I row with the amazing crew at Capital Rowing Club, work on improving my espresso skills, and try to keep my plants alive."